When we compare the African Wild Dog vs Raccoon Dog, we’re talking about two very different creatures. The African wild dog, with only about 6,000 individuals left in the wild, is highly endangered. Meanwhile, the raccoon dog has a much larger population, over 10 million globally, making it more abundant. Explore the best flea shampoo for dogs to keep your furry friend free of pests.
Although both belong to the canid family, their lifestyles are quite different. The African wild dog lives in savannas and woodlands in sub-Saharan Africa, while the raccoon dog is found in forests and suburban areas. These differences make their behavior and survival strategies unique.
Quick Navigation
What are the main differences in hunting techniques between African wild dogs and raccoon dogs?
The main difference in hunting techniques between African wild dogs and raccoon dogs lies in their social structure and hunting style. African wild dogs hunt in highly coordinated packs, using teamwork to chase and exhaust prey over long distances. Their strategy is to target medium-sized ungulates and wear them down with stamina.
In contrast, raccoon dogs are solitary or in small family groups and do not hunt large prey. Instead, they are opportunistic feeders, foraging for small mammals, insects, and fruits, and scavenging from human settlements. Raccoon dogs rely on stealth and adaptability rather than endurance-based hunting. Understand why using human shampoo on dogs might not be the best choice for their skin health.
Comparison Table
African Wild Dog vs Raccoon Dog
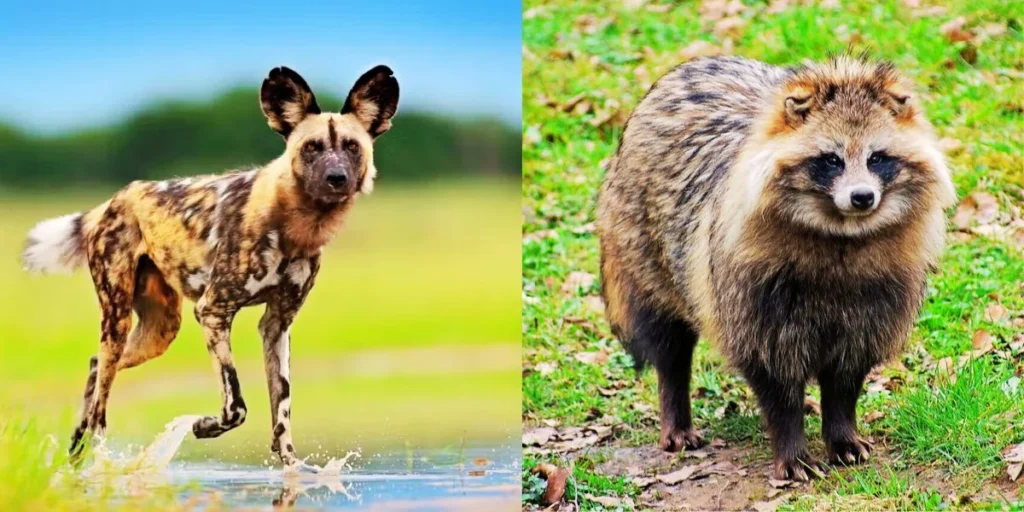

Physical Characteristics
Let’s dive into the physical features of both the African wild dog vs raccoon dog. It’s fascinating how different these two creatures look, even though they both belong to the canid family.
African Wild Dog
The African wild dog is an impressive creature. They stand 24 to 30 inches tall at the shoulder and weigh around 40 to 80 pounds. These dogs have long, slender bodies built for speed and stamina, making them exceptional hunters.
Raccoon Dog
In contrast, the raccoon dog is much smaller. Standing around 17 to 22 inches tall, they typically weigh between 10 to 20 pounds. With their bushy tail and raccoon-like face, they have a distinctive look that sets them apart from most canids, making the African Wild Dog vs Raccoon Dog comparison quite striking.
Coat and Colors
When it comes to fur, African wild dogs have a patchy coat that ranges from light brown to yellow, with black and white patterns. These color variations help them blend into the African savanna, where they hunt. On the other hand, the raccoon dog’s thick, grizzled fur is perfect for colder climates, and its “mask” around the eyes adds to its signature look.
Habitat and Range
Let’s dive into where these two fascinating animals call home. When comparing African Wild Dog vs Raccoon Dog, both have unique habitat preferences that suit their lifestyles. Here’s how they stack up.
African Wild Dog
The African Wild Dog is native to sub-Saharan Africa. They thrive in savannas, woodlands, and open plains, with territories often stretching across 1,000 square kilometers. These dogs need plenty of space for their pack to hunt and roam.
Raccoon Dog
On the other hand, the Raccoon Dog has a much broader range. Native to East Asia, it can be found across China, Korea, and Japan, and has also spread to parts of Europe. Its habitat includes woodlands, forests, wetlands, and even suburban areas, where it can adapt well to human settlements.
The Need for Space
What’s interesting is how each animal’s need for space differs. The African Wild Dog requires large, open spaces to support its pack structure and hunting practices, while the Raccoon Dog is more flexible, often thriving in forested areas or areas near human settlements. It’s fascinating how these animals have adapted to their environments! Discover how Dobermans and Rottweilers compare in terms of personality and traits in Doberman Dog vs Rottweiler.
Diet and Hunting Methods
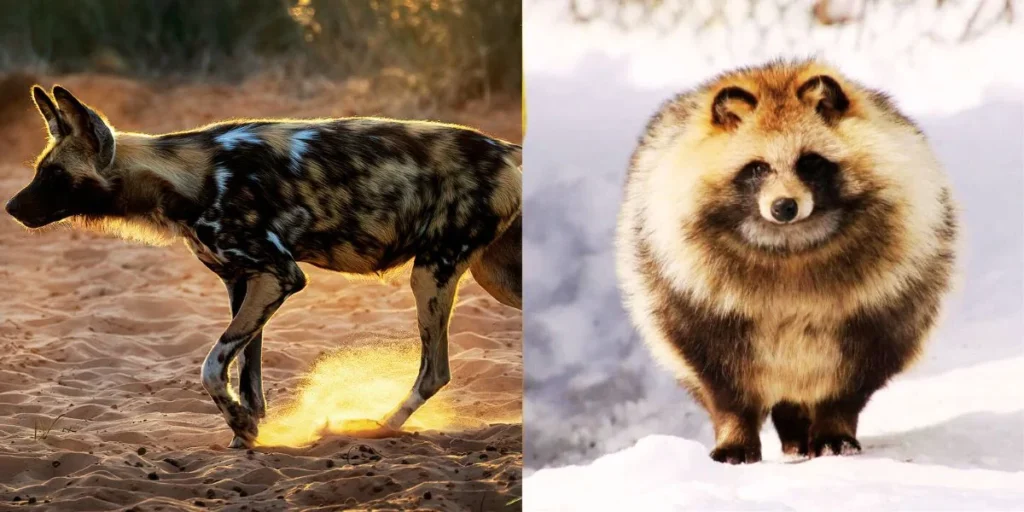

When it comes to their diets, the African Wild Dog and Raccoon Dog take completely different approaches. While the African Wild Dog is a skilled predator, the Raccoon Dog is much more of an opportunistic feeder, adapting to whatever food it can find.
African Wild Dog
The African Wild Dog is a carnivore through and through, and it relies on its pack to catch prey. They primarily hunt medium-sized ungulates like antelopes, often running down animals as large as 100–150 pounds. With hunting success rates of up to 80%, these dogs are incredibly effective when they work together.
Raccoon Dog
In contrast, the Raccoon Dog is an omnivore, meaning it’s not picky about what it eats. Their diet is diverse, including fruits, insects, small mammals, and even birds. It’s common for them to forage alone, foraging up to 2–3 miles a night to find food, especially in forested and suburban areas.
Cooperative vs. Solo Hunting
The difference in their hunting methods is stark. African Wild Dogs are highly social and hunt in teams of 2–20, coordinating their efforts to tire out their prey. On the other hand, Raccoon Dogs tend to scavenge alone, hunting smaller prey or finding food in trash bins, which means they don’t need to share their meals.
Behavior and Social Structure
In this section, we’ll dive into the social lives of the African wild dog and raccoon dog. You’ll see how these two canid species differ in how they interact with their environment and each other.
African Wild Dog
African wild dogs are incredibly social animals, and their pack structure is central to their survival. A pack typically consists of 2 to 27 members, all working together to hunt and protect one another. The bond between these dogs is strong, and they use vocalizations, body language, and scent marking to communicate within the pack.
Raccoon Dog
Unlike the African wild dog, the raccoon dog is more solitary or lives in small family groups. These animals are often nocturnal, and their behavior is marked by a preference for stealth. You won’t typically find raccoon dogs cooperating in groups; they’re more about foraging alone and adapting to their environment quietly.
Communication: A World of Difference
When it comes to communication, African wild dogs are loud and clear. They have a wide range of vocalizations, and their social dynamics rely heavily on these sounds. Raccoon dogs, on the other hand, tend to be more reserved, relying on body language and scent to get their point across.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Let’s dive into the reproduction and lifespan of both the African wild dog and the raccoon dog. These factors reveal a lot about how they live and survive in the wild.
African Wild Dog
The African wild dog has a very organized breeding structure. A single dominant pair in a pack usually does all the breeding, and their pups are born in litters of 2–16. After about 70 days of gestation, pups are born in hidden dens, where they stay for several weeks.
What’s really interesting is the communal care that these pups receive. Even non-breeding adults in the pack help raise the pups, providing food and protection. In the wild, African wild dogs can live up to 10 years, but many face threats that shorten their lives.
Raccoon Dog
On the other hand, the raccoon dog has a different approach to reproduction. They breed once a year, typically producing 4–6 pups per litter. Their gestation period lasts about 60–70 days, and they usually give birth in dens or sheltered areas to protect their young.
Raccoon dogs tend to have a shorter lifespan, averaging 3–5 years in the wild, though they can live up to 10 years in captivity. Despite their relatively short lives, they’re adaptable and can thrive in a variety of habitats. Find out how antifungal shampoo for dogs can protect your pet from skin infections.
Conservation Status
When it comes to conservation, both the African wild dog and raccoon dog have very different challenges to face. While one is critically endangered, the other deals with population pressures but in unique ways. Let’s explore both of their conservation statuses in detail.
African Wild Dog: Endangered
The African wild dog is classified as endangered, with an estimated population of only about 6,000 individuals left in the wild. These dogs face serious threats, including habitat loss, disease, and human-wildlife conflict. Because they require large territories, the fragmentation of their habitats poses a significant barrier to their survival.
Threats to African Wild Dogs
One of the biggest threats to the African wild dog is disease, particularly rabies and distemper, which spread from domestic animals. They also face competition from other carnivores, such as lions and hyenas, that often push them out of their territories. Human encroachment and retaliatory killings for livestock losses further jeopardize their future.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation programs are working hard to protect the African wild dog by creating safe spaces for them, such as wildlife reserves. There are also ongoing efforts to vaccinate dogs and manage disease outbreaks in areas where wild dogs live. In places like Botswana, there are strong protection measures, ensuring that these animals can thrive without constant threats from humans.
Raccoon Dog: Less Endangered but Threatened
Unlike the African wild dog, the raccoon dog is not classified as endangered, but that doesn’t mean it’s free from danger. Its population is stable in many parts of its native range, but it faces threats in some areas due to overhunting and habitat loss. In some regions, they are considered a pest due to their tendency to invade human settlements.
The Invasive Issue in Europe
In Europe, where raccoon dogs were introduced, they have become an invasive species, outcompeting native wildlife. These dogs are now present in countries like Finland and Russia, where they pose a threat to smaller mammals and birds. In these areas, raccoon dogs are culled to protect local ecosystems, which has led to a decline in their numbers in some parts of Europe.
Conservation and Management of Raccoon Dogs
While the raccoon dog isn’t endangered, conservationists are focusing on managing their population in non-native areas to prevent further ecological imbalance. In their native regions, however, raccoon dogs continue to thrive in forests and wetlands. Protection efforts are still crucial to maintain the balance of ecosystems where they live.
Ecological Role
In this section, let’s dive into how these two canids impact the ecosystems they inhabit. Both the African Wild Dog and the Raccoon Dog play significant roles, but in very different ways.
African Wild Dog: Apex Predator in Action
The African Wild Dog is one of the top predators in its habitat. With only about 6,000 individuals left in the wild, it helps maintain the balance by keeping herbivore populations in check. Their cooperative hunting style allows them to hunt in packs and tackle prey much larger than themselves.
Raccoon Dog: Scavenger Extraordinaire
On the other hand, the Raccoon Dog is a scavenger. This canid helps clean up the environment by feeding on a wide variety of food, including insects, small mammals, and fruits. While they aren’t as predatory as African Wild Dogs, they still play a key role in reducing waste and controlling smaller prey populations.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
Interestingly, both species affect their local ecosystems in ways that are crucial to maintaining balance. The African Wild Dog keeps herbivore populations at healthy levels, preventing overgrazing. Meanwhile, the Raccoon Dog helps control smaller species, though it can also disrupt ecosystems when invasive, as seen in parts of Europe.
Raccoon Dogs: An Invasive Threat
While the Raccoon Dog can be beneficial in native environments, in places like Finland and Russia, they are considered an invasive species. They have been known to outcompete native predators, such as foxes, by eating similar food and occupying overlapping territories. This can lead to a decline in biodiversity.
The Wild Dogs’ Ecosystem Contribution
In contrast, the African Wild Dog is crucial in the fight against competitive carnivores. Its hunting habits push smaller predators, like jackals, out of key territories. This process is vital for maintaining a healthy predator-prey balance across vast African landscapes. Learn about the key differences and similarities between these two breeds in our article, Rottweiler Dog vs German Shepherd.
Human Interaction
Human interaction with the African wild dog and raccoon dog varies greatly due to their different behaviors and environments. While one is facing increasing threats from human activity, the other is adapting to urban spaces.
African Wild Dog: Conflict with Humans
African wild dogs often find themselves in conflict with humans, especially in agricultural areas. In fact, these dogs are known to kill livestock, which has led to retaliatory killings by farmers. There are roughly 6,000 African wild dogs left in the wild, and many face death due to human-wildlife conflict.
Despite these challenges, they are rarely aggressive toward people, but their territory overlaps with human settlements. Because of this, conservation efforts are crucial to prevent their extinction, such as the relocation of farmers and communities away from wild dog habitats. It’s estimated that only 14% of the African wild dog population lives in protected areas.
Raccoon Dog: Urban Adaptability
On the other hand, raccoon dogs have found a way to coexist with humans in some parts of the world. They are not as threatened by human activity as African wild dogs and can be seen scavenging through urban areas. With populations spread across East Asia and even parts of Europe, their adaptability allows them to survive in suburban environments.
These dogs are often considered a nuisance by city dwellers, as they rummage through garbage and even steal food.
Interestingly, their population in parts of Europe has grown significantly due to their introduction in the 20th century, leading to concerns about their impact on native species. In fact, raccoon dogs are estimated to be responsible for a significant percentage of prey loss in some European ecosystems.
Final Words
When comparing the African wild dog vs raccoon dog, it’s clear these two species are quite different. The African wild dog, with fewer than 6,000 individuals left, is an endangered species, living in packs and thriving as an apex predator.
On the other hand, the raccoon dog is more adaptable and less endangered, often found in suburban areas, with populations around 5 million. Both animals play unique roles in their ecosystems, but their differences highlight the importance of understanding wildlife diversity.